GUILDify Web Server - Documentation
Introduction
GUILDify is a web server for phenotypic characterization of genes through biological data integration and network-based prioritization algorithms. Towards the goal of extending our knowledge on the genetic elements underlying various phenotypes (including but not limited to disease phenotypes), we aim to use gene-phenotype associations in the literature in combination with the network-based prioritization methods. Considering the lack of convenient interfaces that bridge many of network-based prioritization algorithms to end users, we present GUILDify, an easy to use web server that assigns genes likelihood scores of involvement for a given keyword (e.g. disease phenotype, functional annotation or in broader terms any phenotypic association) using integrated data from publicly available major biological data repositories (see BIANA and GUILD). The databases integrated by BIANA are referred as BIANA-KB (BIANA knowledge base).Schematic overview
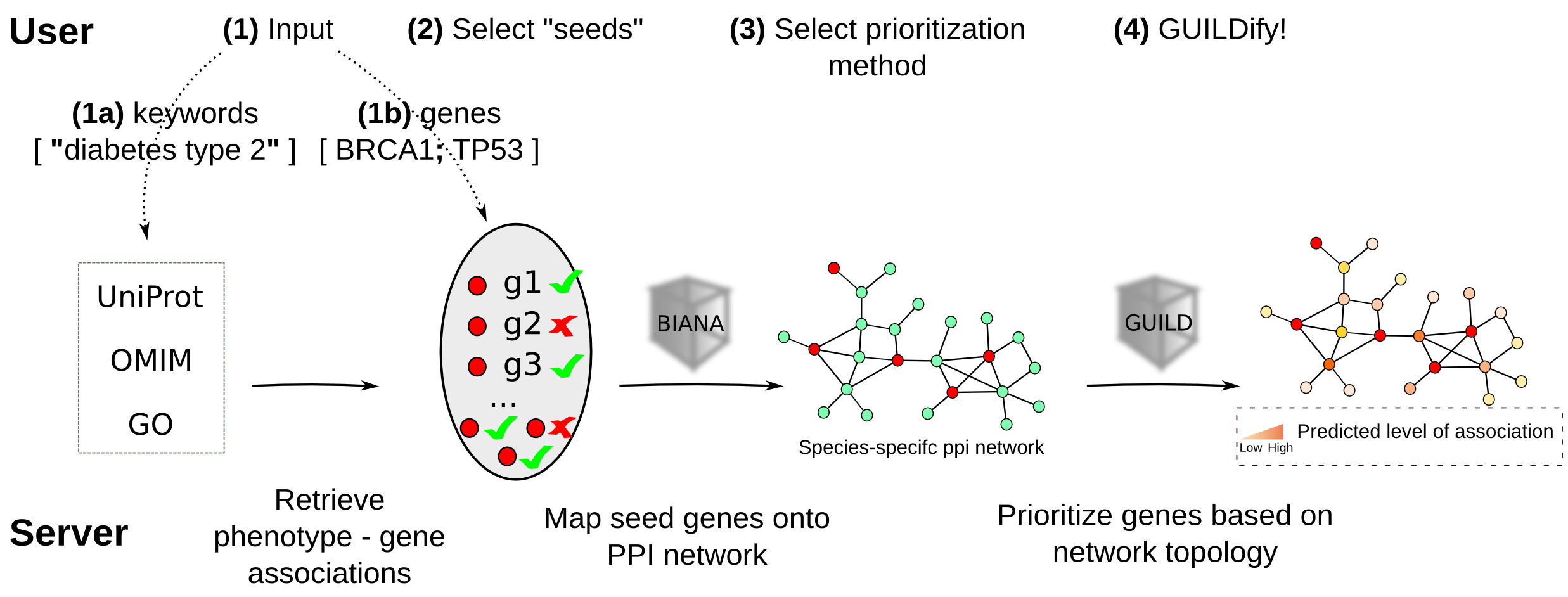
Usage
1- Input: Provide keywords defining a phenotype
Any keyword (or a combination of them) describing a phenotype (i.e. disease, biological function or pathway). A user-provided list of genes can also be queried given that they are separated by semicolons (e.g., "BRCA1;BRCA2").The input form on the home page (shown with A in the figure below), accepts a combination of keywords. If more than one keyword is given (separated by whitespace) these keywords are tried to be matched separately. On the other hand if you want to describe a phenotype that consists of multiple keywords you should add quotation (") around those keywords (e.g. "Alzheimer's disease"). Therefore where "Alzheimer's disease" would only match entries with the occurrences of full text "Alzheimer's disease", Alzheimer's disease (without quotations) would match entries that either contain "Alzheimer's" or "disease". A search in the form of "Alzheimer's disease" alzheimer would match entries that contain either "Alzheimer's disease" (together) or "alzheimer" in the relevant fields of the biological databases integrated by BIANA. Note that, several example keywords are provided (i.e. D in the figure).

The user may choose one of the species listed in the drop box (B in the figure above). Currently the following species are supported: "Homo sapiens", "Mus musculus", "S. cerevisiae", "C. elegans", "D. melanogaster", "A. thaliana" .
Once the keywords are entered and the species is selected, the user can proceed by clicking "Search in BIANA Knowledge base" button (C above).
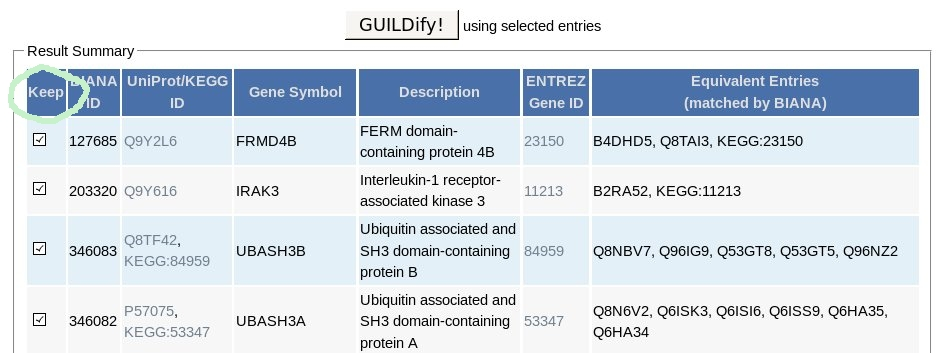
The user may further select which genes to include on the same page by clicking to the check boxes next to the listed entries under the "Keep" column (shown in the image below).
2- GUILDify
First, for the provided keywords, BIANA-KB is queried and the products of the genes (e.g. proteins) associated with these keywords are listed. Relevant fields in these biological data sources such as “description”, “disease”, “function” are looked for keyword matches. At this step, user may choose to use a subset of the listed genes or may provide genes that are not listed by the web server (if there is any). Next, the products of these genes are used as seeds (initial gene-phenotype annotations) and NetCombo method implemented in GUILD framework is run on a species-specific protein-protein interaction network. The resulting scores are then listed along with the descriptive information of the gene products such as UniProt id, gene symbol, Entrez gene id and description.GUILDify is designed to be as simple as possible. Many algorithmic details such as internal parameters used by the scoring algorithms are hidden from the user. These parameters are chosen the values that are shown to be optimum on a large data set of disease phenotypes under the context of GUILD project. Users that are interested in using user-defined parameters are advised to refer to download stand-alone software provided in the aforementioned web page.
3- Status page
The status page provides the links for the result page. This link is going to be available as soon as the scores are calculated by the server. "Access to results" link on this web page can be used go to the result page (when available). In case of a status message of error, please let the webmaster (Emre Guney, email:"name"."surname"@upf.edu) aware attaching relevant information (i.e.the link for the results).4- Output: GUILD scores for association to the phenotype
For each gene product in publicly available databases integrated by BIANA, a likelihood score associating the gene product with the phenotype provided by the user. The likelihood score is the final column in the result table (GUILD Score, shown in the image below). The files containing GUILD Scores of all gene products and seed proteins used in the scoring method can be both downloaded using "Download all scores" and "Download seed proteins" links respectively. The interactome network can also be downloaded using "Download interactome" link.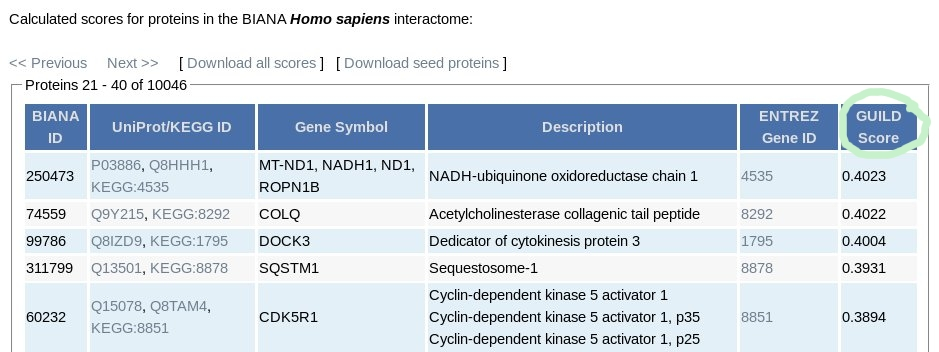
GUILDify also provides an interactive visualization panel for displaying the interactions in the highest scoring subnetwork (highest scoring 1% and 5% proteins and their interactions, see images below). If the species if Homo Sapiens, GUILDify fetches drugs from DrugBank and includes them in the visualization panel. The nodes can be selected in the visualization panel. The information for the selected nodes will be displayed at the bottom of the panel. The drugs can be filtered using the "Include drugs" checkbox. The highest scoring subnetwork and the information on drugs (if the species is Homo Sapiens) can be downloaded using "Download subnetwork" and "Download drug info" links respectively.

