Prothrombin or coagulation factor II synthesised in the liver is a single-chain, vitamin K-dependent glycoprotein belonging to the peptidase S1 family and is present in blood as a precursor.
Prothrombin shares considerable structural similarity with other vitamin K-dependent proteins in blood coagulation, like FVII, FIX, FX and proteins C, S and Z.
Protein Sequence
THRB_BOVIN Prothrombin OS=Bos taurus 625 AA. MARVRGPRLPGCLALAALFSLVHSQHVFLAHQQASSLLQRARRANKGFLEEVRKGNLERE CLEEPCSREEAFEALESLSATDAFWAKYTACESARNPREKLNECLEGNCAEGVGMNYRGN VSVTRSGIECQLWRSRYPHKPEINSTTHPGADLRENFCRNPDGSITGPWCYTTSPTLRRE ECSVPVCGQDRVTVEVIPRSGGSTTSQSPLLETCVPDRGREYRGRLAVTTSGSRCLAWSS EQAKALSKDQDFNPAVPLAENFCRNPDGDEEGAWCYVADQPGDFEYCDLNYCEEPVDGDL GDRLGEDPDPDAAIEGRTSEDHFQPFFNEKTFGAGEADCGLRPLFEKKQVQDQTEKELFE SYIEGRIVEGQDAEVGLSPWQVMLFRKSPQELLCGASLISDRWVLTAAHCLLYPPWDKNF TVDDLLVRIGKHSRTRYERKVEKISMLDKIYIHPRYNWKENLDRDIALLKLKRPIELSDY IHPVCLPDKQTAAKLLHAGFKGRVTGWGNRRETWTTSVAEVQPSVLQVVNLPLVERPVCK ASTRIRITDNMFCAGYKPGEGKRGDACEGDSGGPFVMKSPYNNRWYQMGIVSWGEGCDRD GKYGFYTHVFRLKKWIQKVIDRLGS
Scop Classification:
Class: All beta proteins
Fold: Trypsin-like serine proteases barrel, closed; n=6, S=8; greek-key
Superfamily: Trypsin-like serine proteases
Family: Eukaryotic proteases
Domains:
-
Gla domain
-
Kringle domain
-
Peptidase S1 domain
Prothrombin is activated by FXa to the active two-chain a-thrombin by cleaving the Arg 284-Thr 285 and the Arg 320-Ile 321 peptide bonds, releasing two activation peptides:
a)Fragment 1 (Ala 1-Arg 155) that contains a Gla domain with 10 g-Gla residues and kringle 1.
b)Fragment 2 (Ser 156-Arg 284) that comprise the kringle 2 domain.
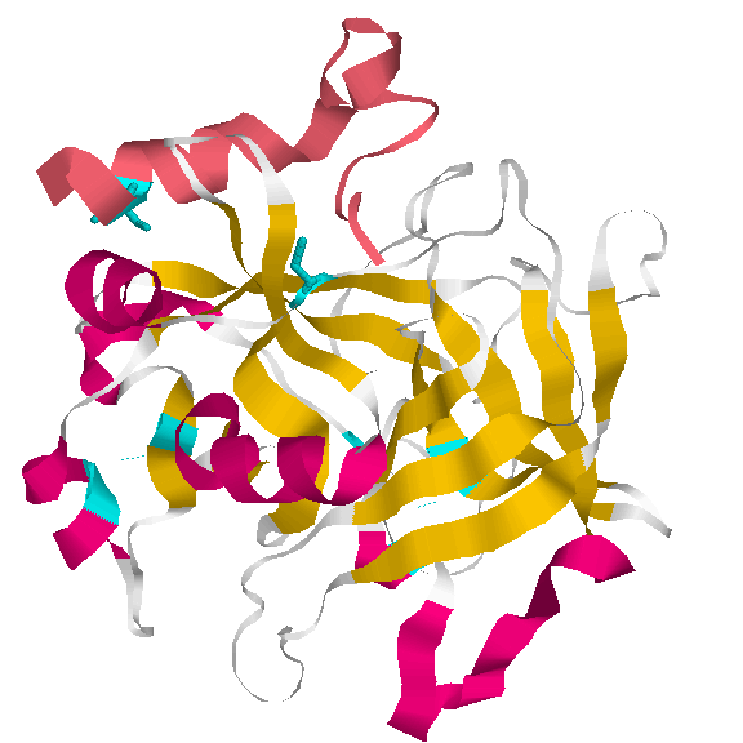
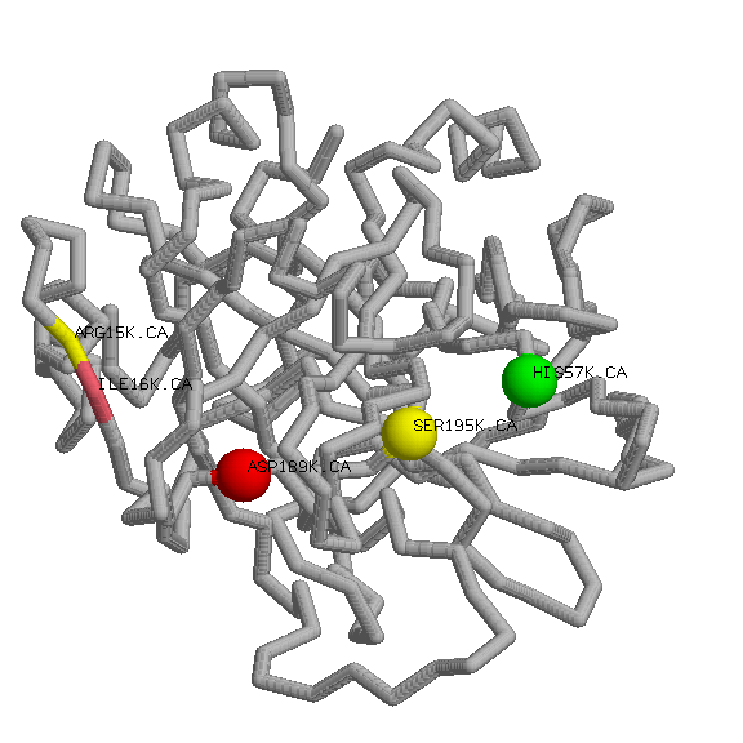
; 1.Cartoons representation bovine thrombin 2.Backbone representation inactive thrombin
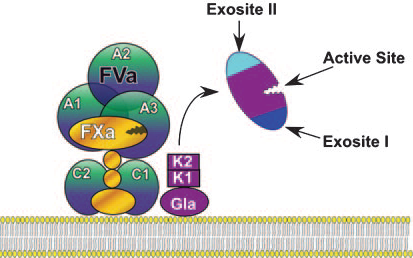
3.Scheme of prothrombin after activation
The Gla Domain are mainly found in the N-terminal region of proteins involved in blood coagulation and fibrinolysis
Sequence:44-90
ANKGFLEEVRKGNLERECLEEPCSR
EEAFEALESLSATDAFWAKYTA
Domain:
Starts at N-terminal and ends with conserved aromatic residue. We find a conserved motif Gla-x(3)-Gla-x-Cys, and clustering of N-terminal hydrophobic residues.
Post-translational modifications of many glutamate residues by vit.K.dependent carboxylation to form Gla. Calcium ions induce conformational changes and are necessary to fold properly.
Function:
The Gla domain is a membrane-binding motif that is required for the binding of coagulation factors to the phospholipid membrane in the presence of calcium ions.
It's hyaluronan-binding domain found in proteins associated with the extracellular matrix,cell adhesion and cell migration.In the presence of calcium ions, interacts with phospholipid membranes that include phosphatidylserine.
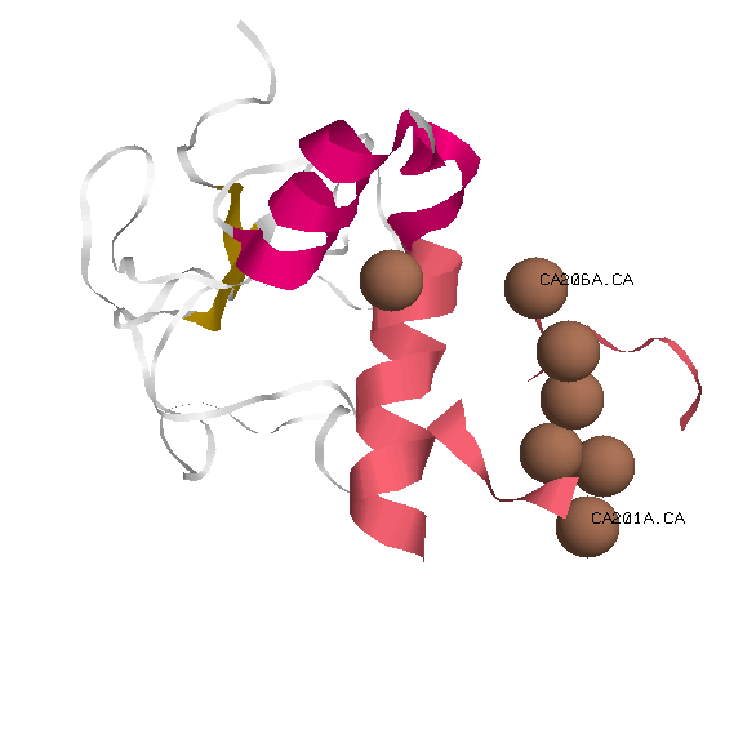
1.Cartoons representationGla domain.
In pink Gla domain with Calcium Ions in brown.
KRINGLE DOMAIN
Kringle domains are mainly found in proteins of blood coagulation and fibrinolysis.
Sequence
In prothrombin we find two kringle domain:
-
Kringle 1 Sequence:108-187
NCAEGVGMNYRGNVSVTRSGIECQ
LWRSRYPHKPEINSTTHPGADLRENFCRNPDGSITg PWCYTTSPTLRREECSVPVC
-
Kringle 2. Sequence:213-292 TCVPDRGREYRGRL
AVTTSGSRCLAWSSEQAKALSK
DQDFNPAVPLAENFCRNPDGDEEg AWCYVADQPGDFEYCDLNY
Domain
The kringle domain is characterised by a triple loop structure of approximately 80 residues with 3 intradomain disulfide bridges.
Function:
Are thought to play a role in binding mediators(e.g. membranes,phospholipids) and in the regulation of proteolytic activity.
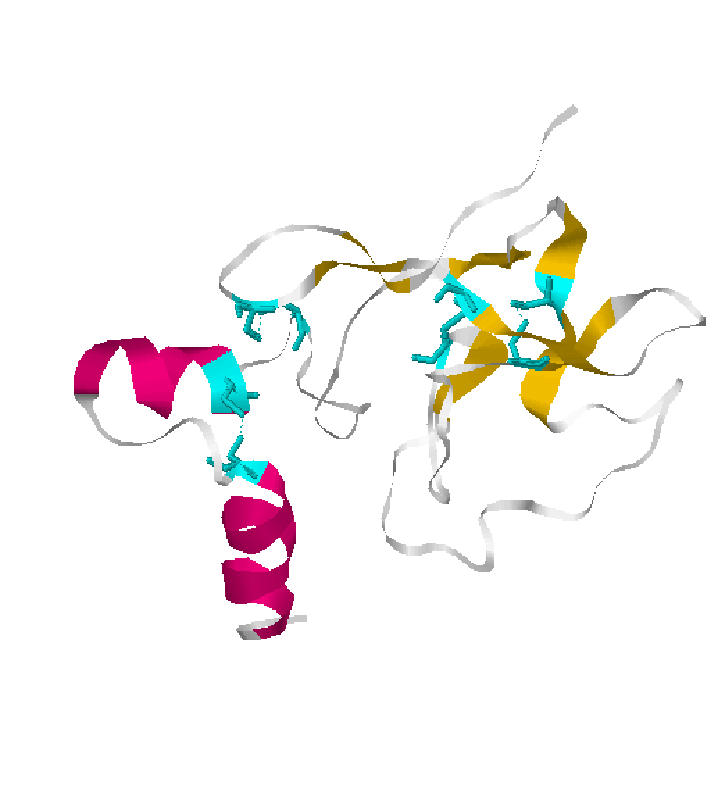
2.Cartoon representations kringle domain and disulfide bridges in cyan color




