Is a plasma glycoprotein synthesised in the liver. It is also a vitamin K-dependent protein and shares considerable structural similarities with other vitamin K-dependent proteins in blood coagulation like FVII, FIX, Prothrombin, proteins C, S and Z, which suggests an evolution from a common ancestral gene.
Factor X is activated into factor Xa by both factor IX (with its cofactor, factor VIII in a complex known as intrinsic Xase) and factor VII with its cofactor, tissue factor (a complex known as extrinsic Xase). It is therefore the first member of the final common pathway or thrombin pathway.
Factor Xa is inactivated by protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor (ZPI), a serine protease inhibitor (serpin). The affinity of this protein for factor Xa is increased 1000-fold by the presence of protein Z, while it does not require protein Z for inactivation of factor XI. Defects in protein Z lead to increased factor Xa activity and a propensity for thrombosis.
In complex with FVa, FXa binds to negatively charged membrane phospholipids in the presence of Calcium ions, cleaving prothrombin in two places (an arg-thr and then an arg-ile bond), which yields the active thrombin, thus leading to the activation of Prothrombin to Thrombin. This process can be done without FVa but this way the process is optimized.
FXa can also activate FVII to FVIIa and can convert cofactor proteins FV to FVa and FVIII to FVIIIa. The main inhibitors of FXa are the antithrombin III, alpha1-antitrypsin and tissue factor pathway inhibitor.
Warfarin and the heparin series of anticoagulants and fondaparinux, act to inhibit the action of Factor Xa in various degrees.
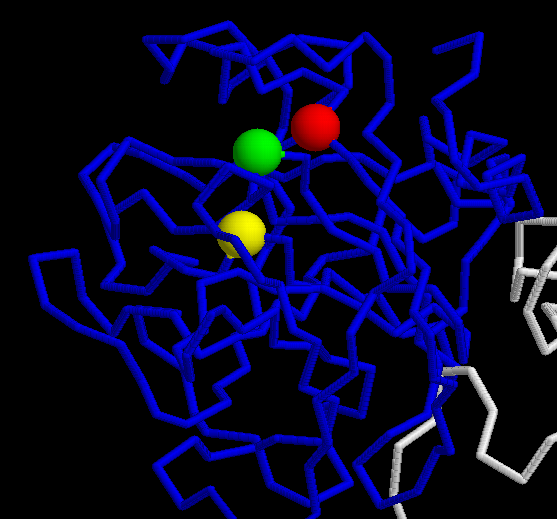
The zymogen FX needs to be binded to Calcium to get activated. The residues of the Gla domain helps that with the collaboration of vitamin K, which carboxilates them.
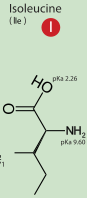
They are implicated in the Calcium binding. The first one is more important than the second.
That corresponds to the active serine protease. When the zymogen is cleaved it is able to interact with the Prothrombin and FVa to activate the first one.
His 275(c57)
Asp 321(c102)
Ser c 418(c195)
The cleavage is done between the 233 (c15) and 234 (c16) aminoacids.
The specifity of the coagulation FX consists in the Exosites I and II included in the Peptidase S1 domain. The first one binds the Ca2+, which is absent from thrombin due to insertion of K70 side chain into this site. Exosite II of FXa is important to Prothrombine substrate recognition and for the critical interaction with FVa.
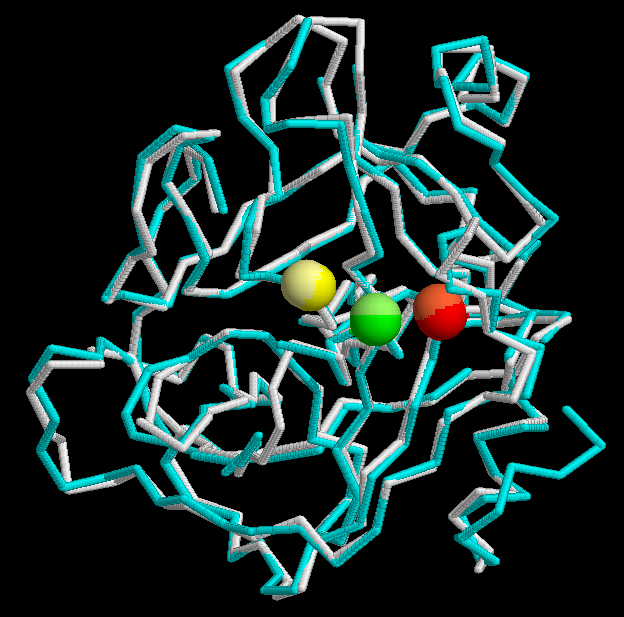
The secondary structure of the FX is only available for the BOS_TAURUS and HUMAN species. In the superposition of that two species it can be observed the similarity of the structures. The active sites match perfectly.
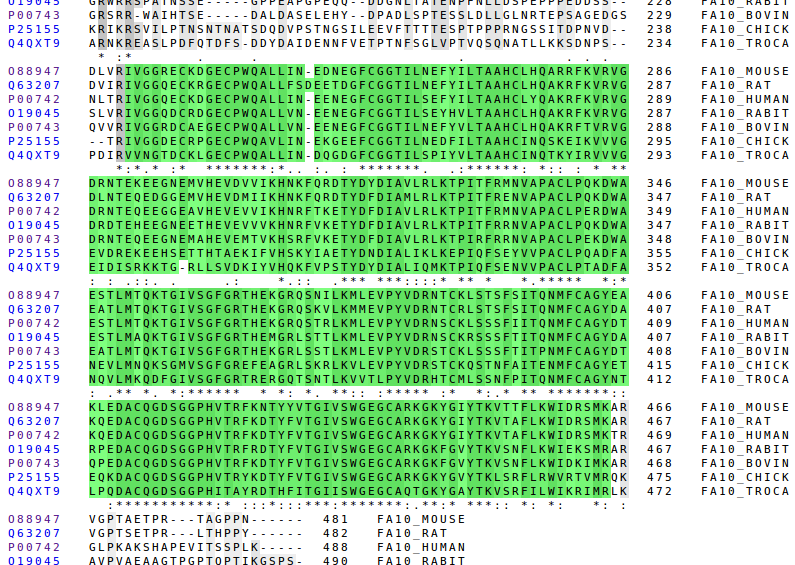
It can also be done the comparison of more species by using its primary structure. We've used the following: mouse, rat, human, rabbit, bovin, chick and tropidechis carinatus (a snacke).
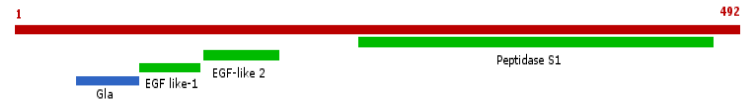
Domains:

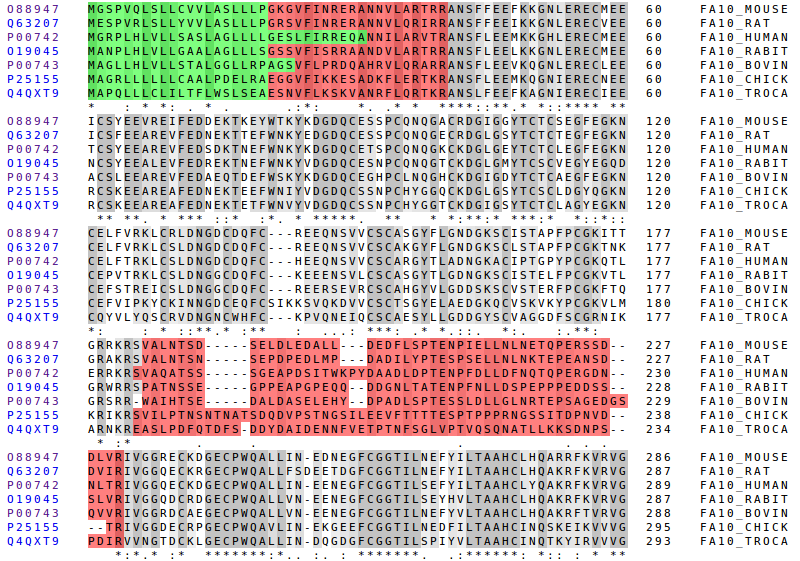
Here we can see the Gla, the EGF-like domains and the Peptidase S1 domain. The better conserved regions are the domains and the signalling parts. That domains are the most functional parts of the protein so they must have been naturally selected.
The position in which the cleavage is done to release free the Peptidase S1 is the same for every especies, it is always RI, except in the case of the snacke which has Val instead of Ile. But the Val has very similar properties to Ile: both are hydrophobic and have a very similar structure.
|
|
Signalling and propeptide regions:
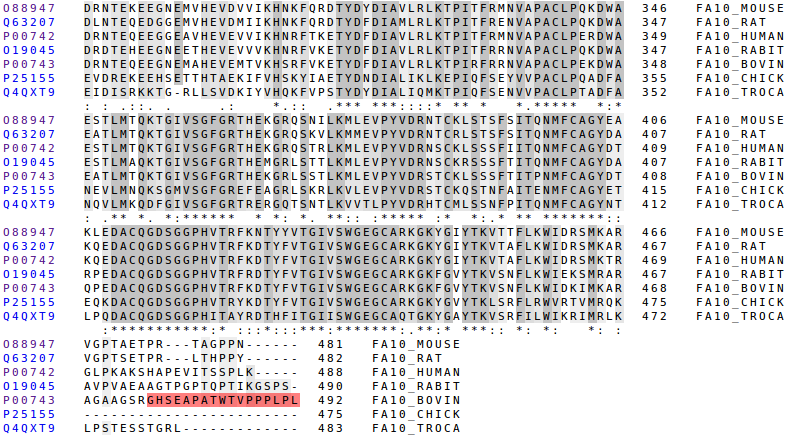
The signalling and the first propeptide region are the better conserved parts, but not as good as the domains. This two parts are also functional, because they are important to recognize the bindings and to do the cleavage. In respect to the second propeptide region it's clearly not very conserved but, there's one important detail to comment: the last aminoacid of that, which corresponds with the cleavage, is perfectly conserved.
The last propeptide region only appears in the bovine. It's an addition to the chain that is not really functional. It has evolved in a way that allows FX to be work properly.
Specificity:
The parts of the Factor X that makes it different from the other coagulation factors are conserved, but not as conserved as the trypsin-like characteristics.
